Products
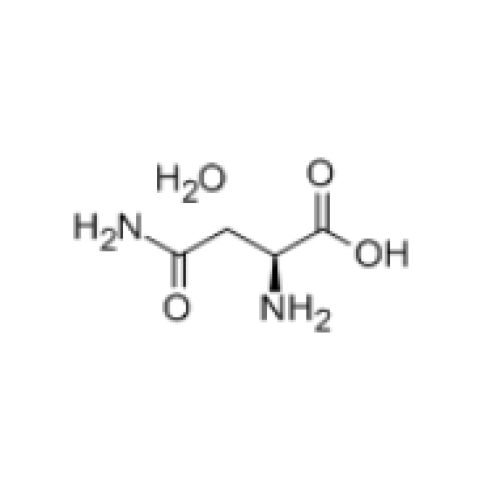
L(+)-Asparagine monohydrate
Use and description |
| Asparagine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain carboxamide, classifying it as a polar, aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it. It is encoded by the codons AAU and AAC. |
Physical Characters and Index |
English name: L (+) - Asparagine monohydrate CAS no. : 5794-13-8 Molecular formula: C4H10N2O4 Molecular weight: 150.13 EINECS no. : 611-593-6 |