
Products
Betaine
Use and description |
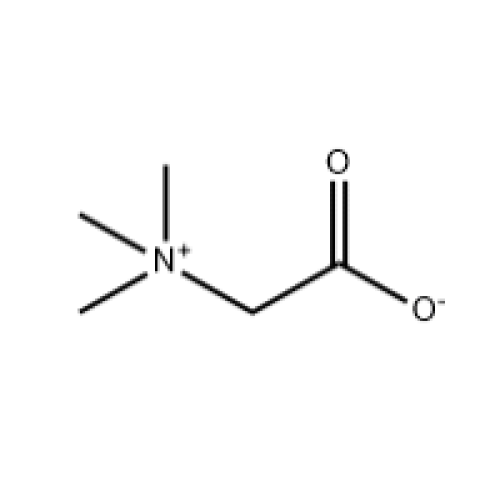
| Betaine is a trimethylglycine and derivative of the nutrient choline. In other words, choline is a “precursor” to betaine and must be present for betaine to be synthesized in the body. It’s created by choline in combination with the amino acid glycine. Just like some B vitamins, including folate and vitamin B12, betaine is considered to be a “methyl donor.” This means it aids in liver function, detoxification and cellular functioning within the body. Its most crucial role is to help the body process fats. |
Physical Characters and Index |
Product Name:Betaine CAS:107-43-7 Molecular Formula:C5H11NO2 Molecular Weight:117.15 Purity:99% Appearance:White or off-white crystalline powder. Melting point:310 °C (dec.) Boiling point:218.95°C (rough estimate) Storage conditions:2-8°C |






![4-[2-(Methylamino)ethyl]phenol hydrochloride](http://www.owaispharm.com/uploadfile/202506/780b5071b849c.png#没有设置高宽参数,将以原图输出)




