Products
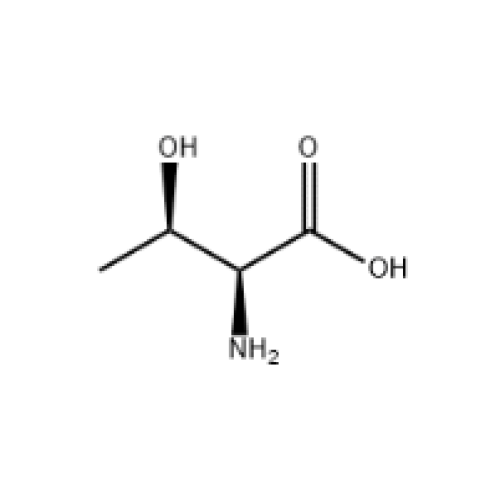
L-Threonine
Use and description |
| Threonine is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as E. coli. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC. |
Physical Characters and Index |
English name: L-Threonine CAS no. : 72-19-5 Molecular formula: C4H9NO3 Molecular weight: 119.12 EINECS no. : 200-774-1 |